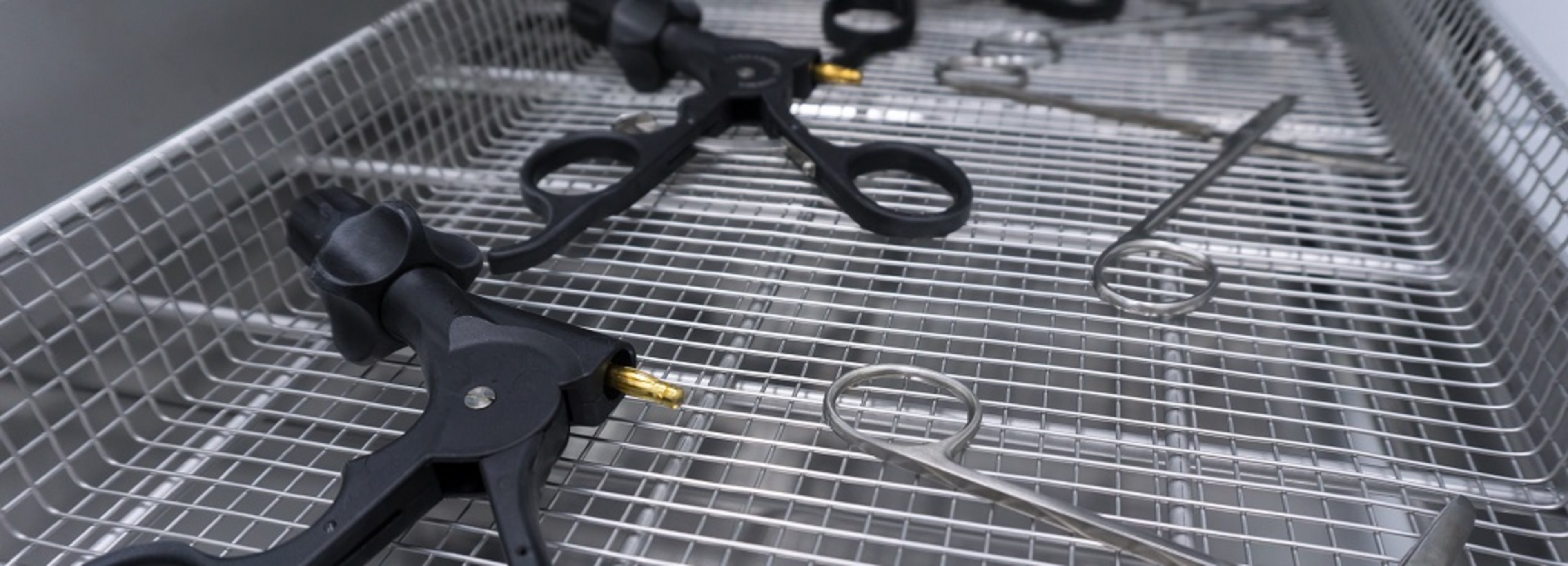
What is "cleaning validation" for medical devices?
The terms "cleaning validation" and "reprocessing validation" are often used interchangeably. It should be noted that these are fundamentally different topics. Cleaning validation involves checking the effectiveness of final cleaning after manufacture. Validation of reprocessing" actually refers to the validation of the reprocessing procedure described in the manufacturer's instructions for reprocessable medical devices. In the following, we present the typical analyses associated with these validations and explain the differences.
The "cleaning validation"
Validation of the final cleaning of medical devices after the manufacturing process
Manufacturers of medical devices are obliged to exclude or minimize all foreseeable risks when used as intended. This also includes risks that may arise after delivery due to a high level of contamination of the product surface, for example due to production residues. The manufacturer must ensure that critical contamination is reduced and that all specified acceptance criteria are met. A validation of the cleaning process must be carried out to prove this.
Objective:
Proof that production residues (e.g. lubricants, particles, cleaning agents, biofilms) have been safely removed after final cleaning.
Typical tests:
- In vitro cytotoxicity test: Detection of chemical/toxic residues
- Bioburden: Germ count determination
- LAL-Test: Detection of endotoxins
- Particle Analysis: Detection of particles by means of OPC (optical particle counter) or microscopically
- TOC (Total Organic Carbon): Detection of organic residues (e.g. polishing agents, surfactants).
- THC (Total Hydrocarbon Content): Detection of hydrocarbon compounds (e.g. oils, coolants and lubricants)
Exemplary causes for increased TOC/THC values:
- Residues from machining oils or polishing pastes.
- Insufficiently removed cleaning agents.
The "reprocessing validation"
Validation of the manufacturer's instructions for reprocessing reusable medical devices (by the manufacturer)
The manufacturer of medical devices must provide the user of these devices with valid and standard-compliant information and instructions for the reprocessing of reusable medical devices. The validation of this information is a process in which it is verified that the manufacturer's reprocessing instructions meet the requirements for safe and effective reprocessing. It verifies that the cleaning, disinfection and sterilization (if required) of the device achieve the intended effect under the specified conditions and that this effect is reproducible. Validation ensures that the device is safe for the patient after reprocessing and complies with the applicable standards and regulations.
The term "reprocessing validation" is also used for the validation of the reprocessing process (cleaning, disinfection and sterilization) by the "reprocessor". This includes hospitals, the private practice sector and external service providers. This involves validated processes as the basis for proper and efficient process organization in the reprocessing unit for medical devices (AEMP). In particular, the technical equipment for reprocessing is validated. However, this validation is not considered below in the context of "reprocessing validation".
Objective:
Ensure that the manufacturer's instructions for reprocessing reusable medical devices are effective and that the contaminated medical devices can be reused hygienically and safely after use.
Typische Analysen:
- Protein residues (e.g. OPA test): Detection of blood or tissue residues.
- Bioburden: Detection of microbial contamination.
- LAL-Test: Detection of endotoxins, especially in products for invasive procedures.
- TOC (Total Organic Carbon): Detection of organic residues (cleaning and disinfectant residues).
- Function test: Ensuring mechanical integrity (e.g. for endoscopes).
- Sterility test: For products to be used sterile.
Summary of the differences
| Feature | Cleaning validation | Validation of the reprocessing instructions |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | Removal of production residues | Removal of biological contamination |
| Responsible | Manufacturing company | Manufacturer/Distributor |
| Typical residues | Oils, polishing agents, cleaning agents | Blood, tissue, microorganisms, cleaning agents and disinfectants |
| Relevant tests | Cytotoxicity, bioburden, THC/TOC, particles, endotoxins | Protein, TOC, bioburden, sterility test |
| Focus | Product safety before packaging | Patient safety before repeated use |
Newsletter registration