Comparison of analytical methods in materials science


The characterization of material composition is an essential part of materials science. It enables the chemical composition of materials to be determined. This white paper compares the two main analytical methods used in the metals industry - optical emission spectrometry (OES) and X-ray fluorescence analysis (XRF) - with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX).
Optical emission spectrometry (OES)
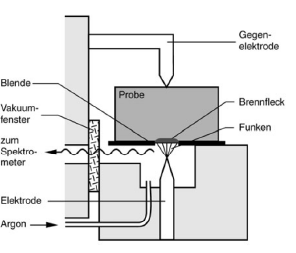
OES is a method for determining the chemical composition of materials in which the light emitted by excited atoms is analyzed. The atoms of the elements present in the metal are brought to a higher energy level by supplying energy (electric arc discharge). The supply of energy initially causes the atoms to jump to free spaces in higher-energy shells. As this state is very unstable, the excited atoms fall back into their shells by emitting light quanta. Based on the existing knowledge of the emission spectra of the elements, the emitted wavelength can be assigned to the respective elements.
Application examples:
- Analysis of the chemical composition of alloys in the metal industry
- Quality control of metallic materials
Advantages and disadvantages:
| Advantage | Disadvantage |
| ➕ High accuracy | ➖ Complex sample preparation |
| ➕ Option for database matching | ➖ Sample geometry must be suitable to cover aperture (min. 6 mm diameter) |
| ➕ Suitable for the analysis of metals of different base alloys | ➖ Destructive material testing |
| ➖ High costs for instruments |
X-ray fluorescence analysis (XRF)
XRF is based on the interaction of X-rays with the sample. The sample is irradiated with X-rays, which emit characteristic fluorescent rays. These characteristic rays for each element are analyzed and quantified to determine the chemical composition of the sample. To determine the proportions of light elements such as carbon, nitrogen, etc., work is carried out under inert gas, such as the noble gas helium.
Application examples
- Determination of the chemical composition of minerals in geology
- Analysis of environmental samples to determine pollutants
Advantages and disadvantages
| Advantage | Disadvantage |
| ➕ Versatile application | ➖ Medium accuracy, especially in the area of light elements |
| ➕ Independent of the sample geometry | ➖ No possibility of database matching |
| ➕ Non-destructive testing | ➖ Sensitive to interference |
| ➕ Less complex sample preparation |
Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX):
EDX is a method for analyzing the chemical composition of materials in which the characteristic X-rays emitted by the sample are examined. For this purpose, the sample is irradiated with an electron beam. The emitted X-rays are captured by a detector depending on the angle. They are then analyzed based on the number of counts received and displayed in a spectrum.
Application examples:
- Examination of the surfaces and near-surface composition of materials
- Analysis of particles and residues, such as corrosion products on metallic surfaces
Advantages and disadvantages:
| Advantage | Disadvantage |
| ➕ High accuracy | ➖ Limited penetration depth and analysis area |
| ➕ No database matching for alloy compositions | ➖ High costs for equipment |
| ➕ Non-destructive testing depending on sample size and preparation | |
| ➕ Analysis of organic samples after suitable preparation |
The methods in comparison
| Method | Accuracy | Detection limit | Sample preparation | Application areas |
OES | ➕➕ high | ➕➕ low | ➖ complex | ➕ metal analysis |
XFA | ➕ medium | ➕ medium | ➕➕ less complex | ➕➕ versatile |
EDX | ➕➕ high | ➕➕ low | ➕➕ less complex | ➕ surface analysis |
Conclusion
The choice of suitable analysis method depends on the specific application and the requirements for accuracy and detection limits. OES is particularly suitable for metal analysis, while XRF is versatile and EDX is suitable for surface analysis. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, which should be taken into account when making a selection.
Newsletter registration